State Management Example Bot
In this example section, we will create a bot that demonstrates Telegram's state management system. The bot will guide users through a multi-step conversation to collect their name and age, using states to maintain context between interactions.
We will use the following handlers:
onMessagewithfilter.commands()or@MessageHandlerwithcommandparameter for command triggersonMessagewithfilter.state()or@MessageHandlerwithstateparameter for state-specific message handling
Import necessary classes
package io.github.natanimn;
import io.github.natanimn.telebof.BotClient;
import io.github.natanimn.telebof.BotContext;
import io.github.natanimn.telebof.enums.ParseMode;
import io.github.natanimn.telebof.enums.MessageType;
import io.github.natanimn.telebof.annotations.MessageHandler;
import io.github.natanimn.telebof.types.updates.Message;
Create StateExampleBot class and initialize BotClient with state handlers
public class StateExampleBot {
BotClient bot;
public StateExampleBot(String token){
bot = new BotClient(token);
// Register handlers for different states and commands
bot.onMessage(filter -> filter.commands("start"), this::start);
bot.onMessage(filter -> filter.commands("cancel") && filter.state("*"), this::cancel);
bot.onMessage(filter -> filter.state("name") && filter.text(), this::getName);
bot.onMessage(filter -> filter.state("age") && filter.text(), this::getAge);
}
}
Our bot will manage the following conversation flow using states:
- /start command → Sets state to
"name"and asks for user's name - User provides name → Sets state to
"age"and asks for age - User provides age → Processes both pieces of information and clears state
- /cancel command → Clears current state at any point in the conversation
State Handlers Implementation
1. Start Handler - Initiating the Conversation
The /start command begins the multi-step interaction by setting the initial state.
@MessageHandler(commands = "start")
private void start(BotContext ctx, Message message){
// Ask for the user's name
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id, "Hey! What is your name?").exec();
// Set the user's state to "name" to indicate we're expecting their name next
ctx.setState(message.from.id, "name");
}
Explanation:
setState(user_id, "name")marks that this user is now in the "name" state- The next message from this user will be processed by the
getNamehandler
2. Name Handler - Collecting the Name
This handler is triggered when a user in the "name" state sends any message.
private void getName(BotContext ctx, Message message){
// Ask for the user's age
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id, "How old are you?").exec();
// Transition to the "age" state
ctx.setState(message.from.id, "age");
// Store the provided name in state data for later use
var data = ctx.getStateData(message.from.id);
data.put("name", message.text);
}
filter.state("name")ensures this handler only processes messages from users in the "name" statefilter.text()ensures that user only entertextgetStateData(user_id)retrieves a Map where we can store temporary conversation datadata.put("name", message.text)saves the user's name for the final summary
@MessageHandler(type = MessageType.TEXT, state = "name")
private void getName(BotContext ctx, Message message){
// Ask for the user's age
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id, "How old are you?").exec();
// Transition to the "age" state
ctx.setState(message.from.id, "age");
// Store the provided name in state data for later use
var data = ctx.getStateData(message.from.id);
data.put("name", message.text);
}
Key Concepts:
state = "name"ensures this handler only processes messages from users in the "name" statetype = MessageType.TEXTensures that user only entertextgetStateData(user_id)retrieves a Map where we can store temporary conversation datadata.put("name", message.text)saves the user's name for the final summary
3. Age Handler - Collecting and Processing Age
This handler processes messages from users in the "age" state.
private void getAge(BotContext ctx, Message message){
int age;
// Validate that the input is a number
try {
age = Integer.parseInt(message.text);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id, "Please enter a valid number").exec();
return; // Stay in the "age" state until valid input is provided
}
// Retrieve the stored name from state data
var data = ctx.getStateData(message.from.id);
// Send confirmation message
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id, "Thank you for the information you have provided.").exec();
// Display the collected information
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id,
String.format("<b>Name:</b> %s\n<b>Age:</b> %d", data.get("name"), age))
.parseMode(ParseMode.HTML)
.exec();
// The state is automatically cleared after the conversation completes
ctx.clearState(message.from.id);
}
@MessageHandler(state = "age", type = MessageType.TEXT)
private void getAge(BotContext ctx, Message message){
int age;
// Validate that the input is a number
try {
age = Integer.parseInt(message.text);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id, "Please enter a valid number").exec();
return; // Stay in the "age" state until valid input is provided
}
// Retrieve the stored name from state data
var data = ctx.getStateData(message.from.id);
// Send confirmation message
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id, "Thank you for the information you have provided.").exec();
// Display the collected information
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id,
String.format("<b>Name:</b> %s\n<b>Age:</b> %d", data.get("name"), age))
.parseMode(ParseMode.HTML)
.exec();
// The state is automatically cleared after the conversation completes
ctx.clearState(message.from.id);
}
Explanation:
- Input validation ensures we get a valid age before proceeding
data.get("name")retrieves the name stored in the previous step- The state is automatically handled by the framework after completion
4. Cancel Handler - Aborting the Conversation
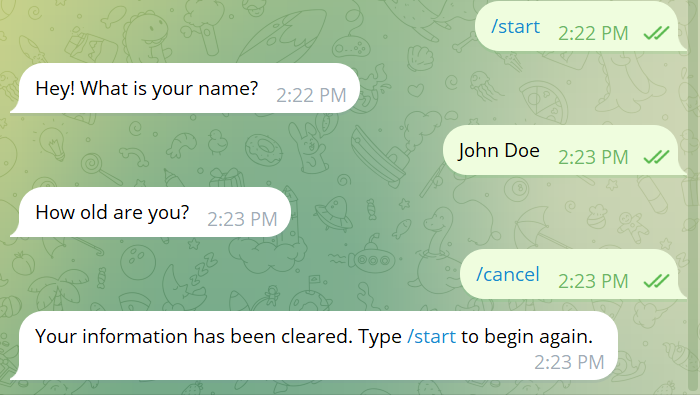
The /cancel command can be used at any point to abort the current conversation.
private void cancel(BotContext ctx, Message message){
// Clear the user's current state and any stored data
ctx.clearState(message.from.id);
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id,
"Your information has been cleared. Type /start to begin again.").exec();
}
Key Feature:
filter.state("*")matches users in any active state, allowing cancellation from any stepclearState(user_id)removes both the state marker and any associated data
@MessageHandler(commands = "cancel", state = "*", priority = -1)
private void cancel(BotContext ctx, Message message){
// Clear the user's current state and any stored data
ctx.clearState(message.from.id);
ctx.sendMessage(message.from.id,
"Your information has been cleared. Type /start to begin again."
).exec();
}
state = "*"matches users in any active state, allowing cancellation from any steppriority = -1registered and executed before all handlersclearState(user_id)removes both the state marker and any associated data
Running the Bot
public void run(){
bot.startPolling();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
var token = System.getenv("TOKEN"); // Get token from environment variable
var state_bot = new StateExampleBot(token);
state_bot.run();
}
Conversation Flow Example
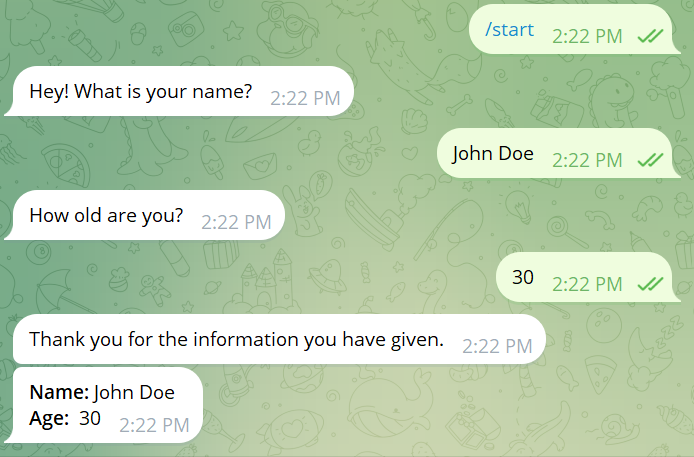
- User sends
/start→ Bot sets state to"name"and asks for name - User provides name → Bot stores name, sets state to
"age", asks for age - User provides age → Bot displays collected information
- (Optional) User can send
/cancelat any time to abort the process
The full source code can be found on examples/state_bot